I. About
- An expense tracking application proving CRUD using React.
- Github:
Chart1: Create
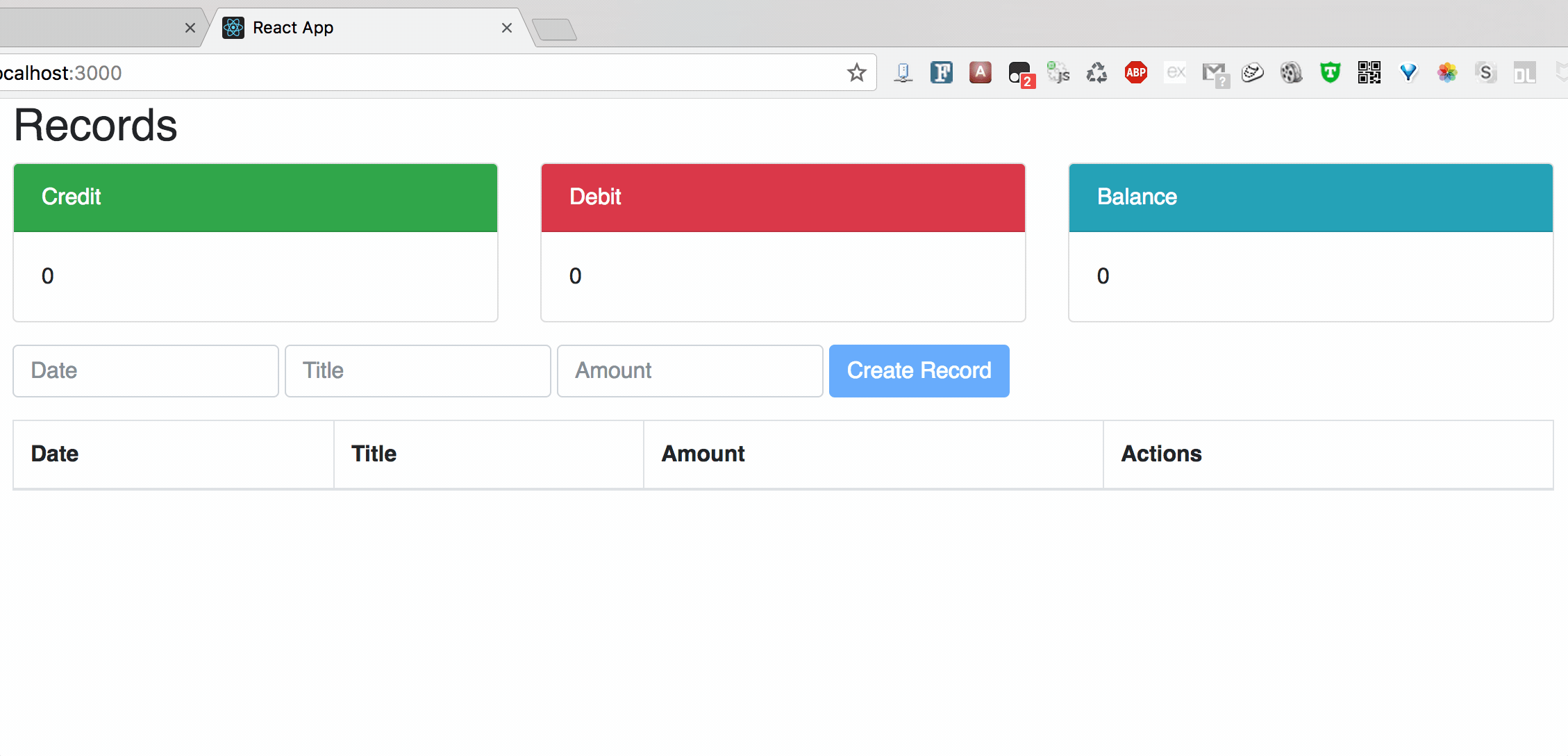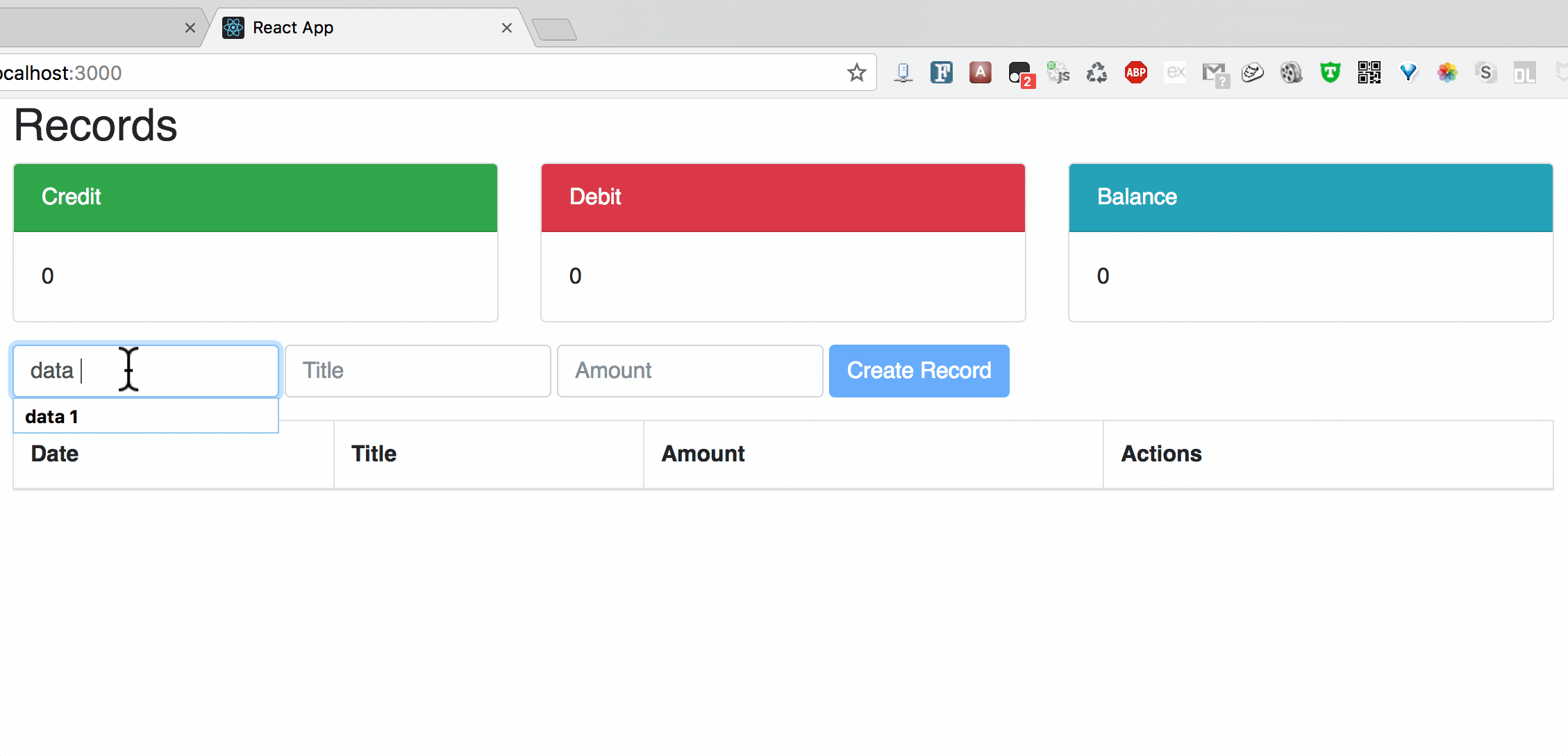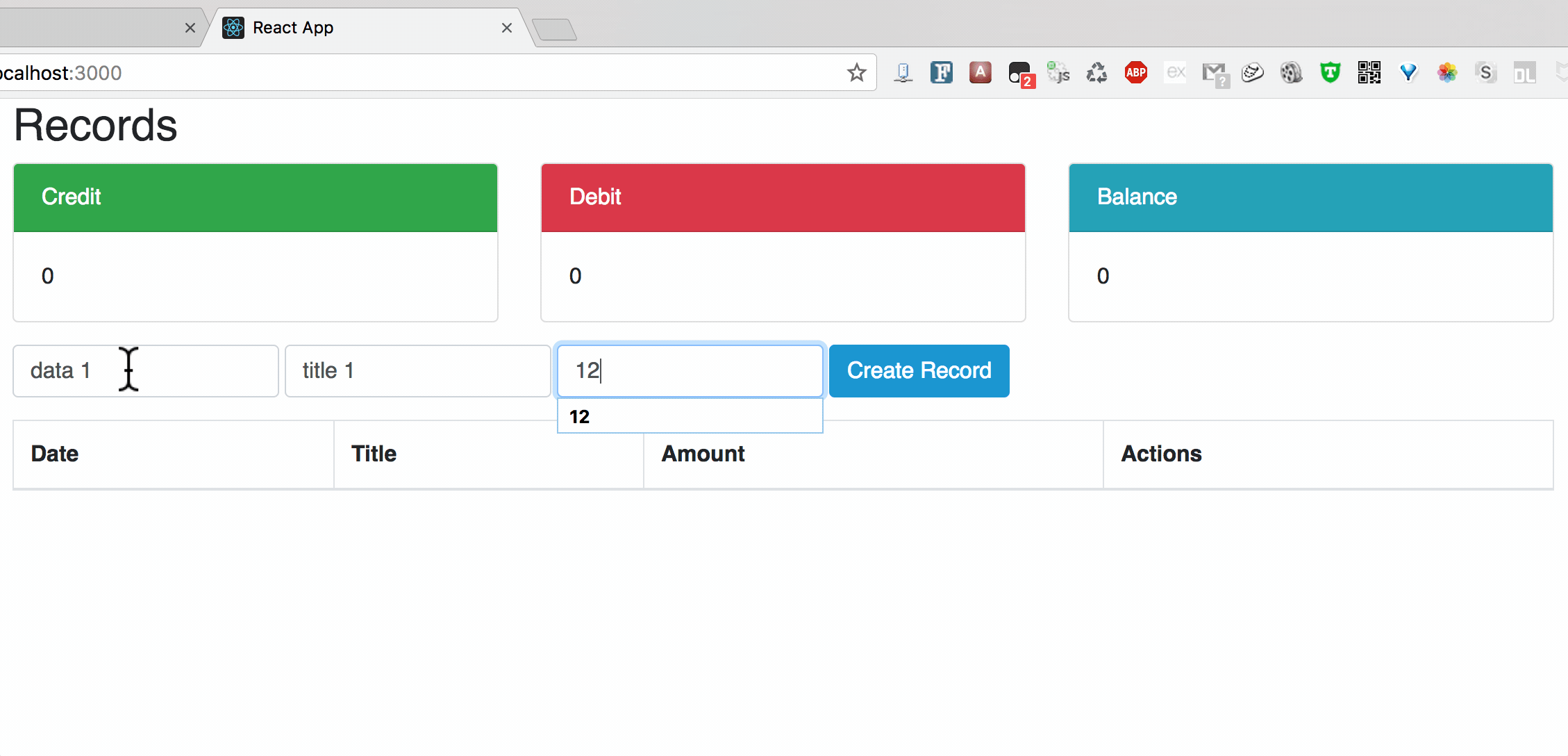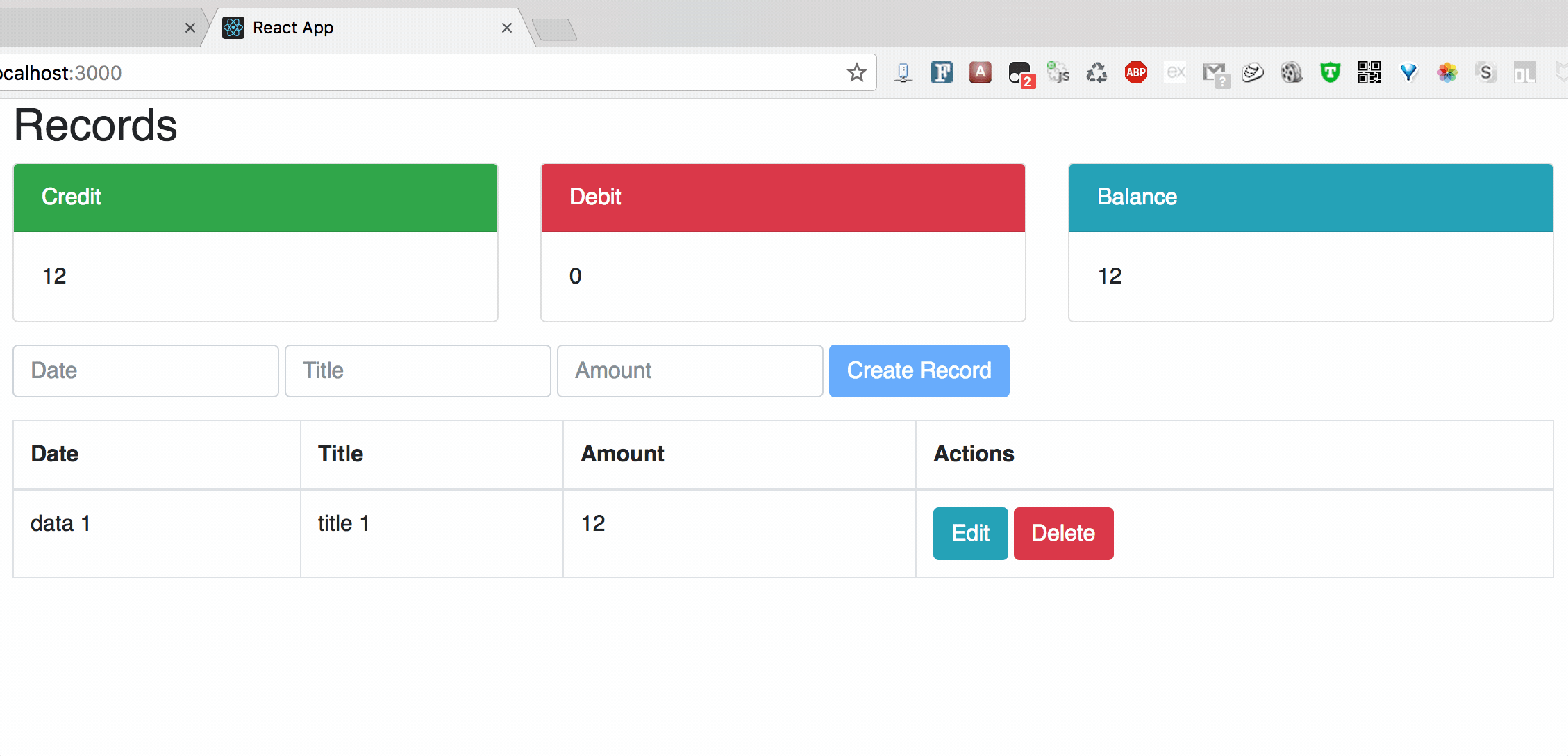
**Chart2: Update
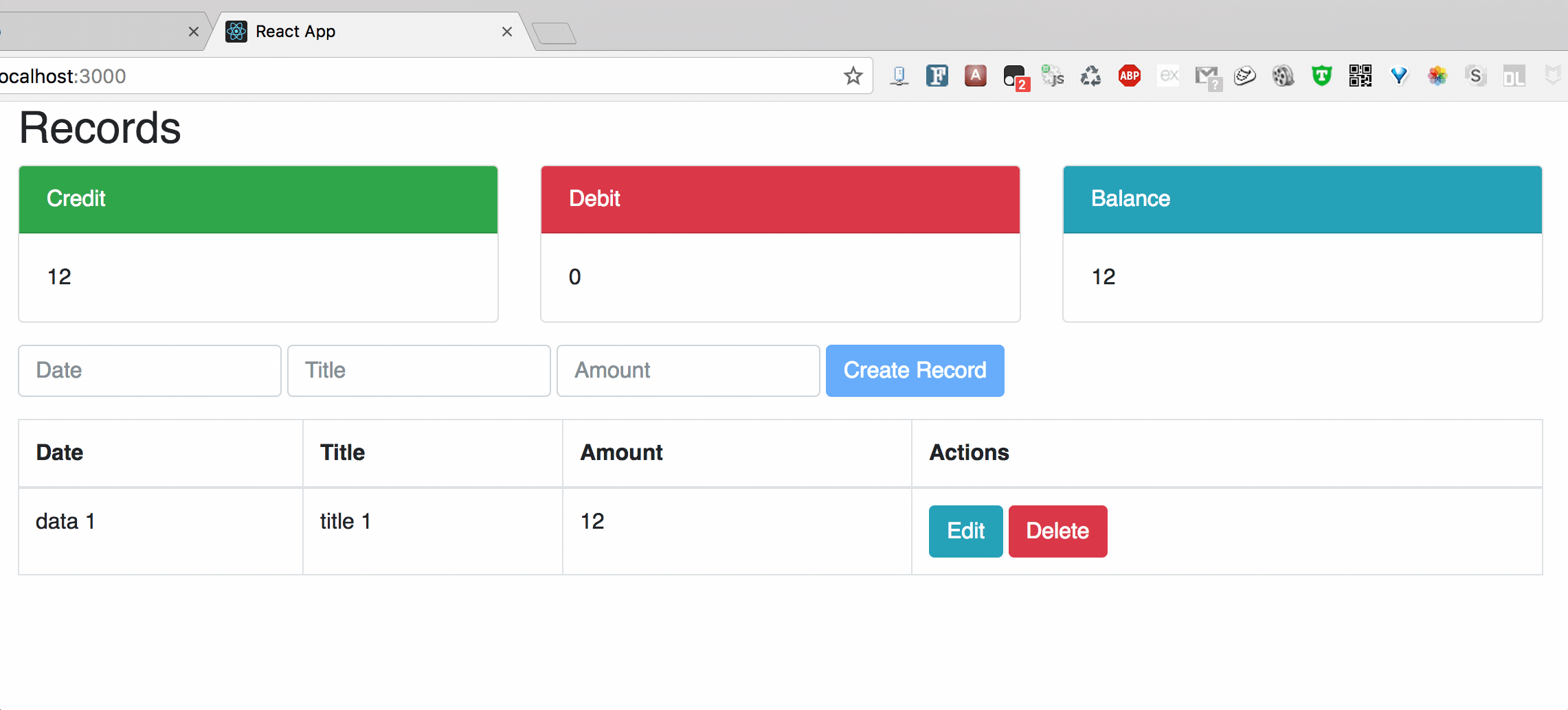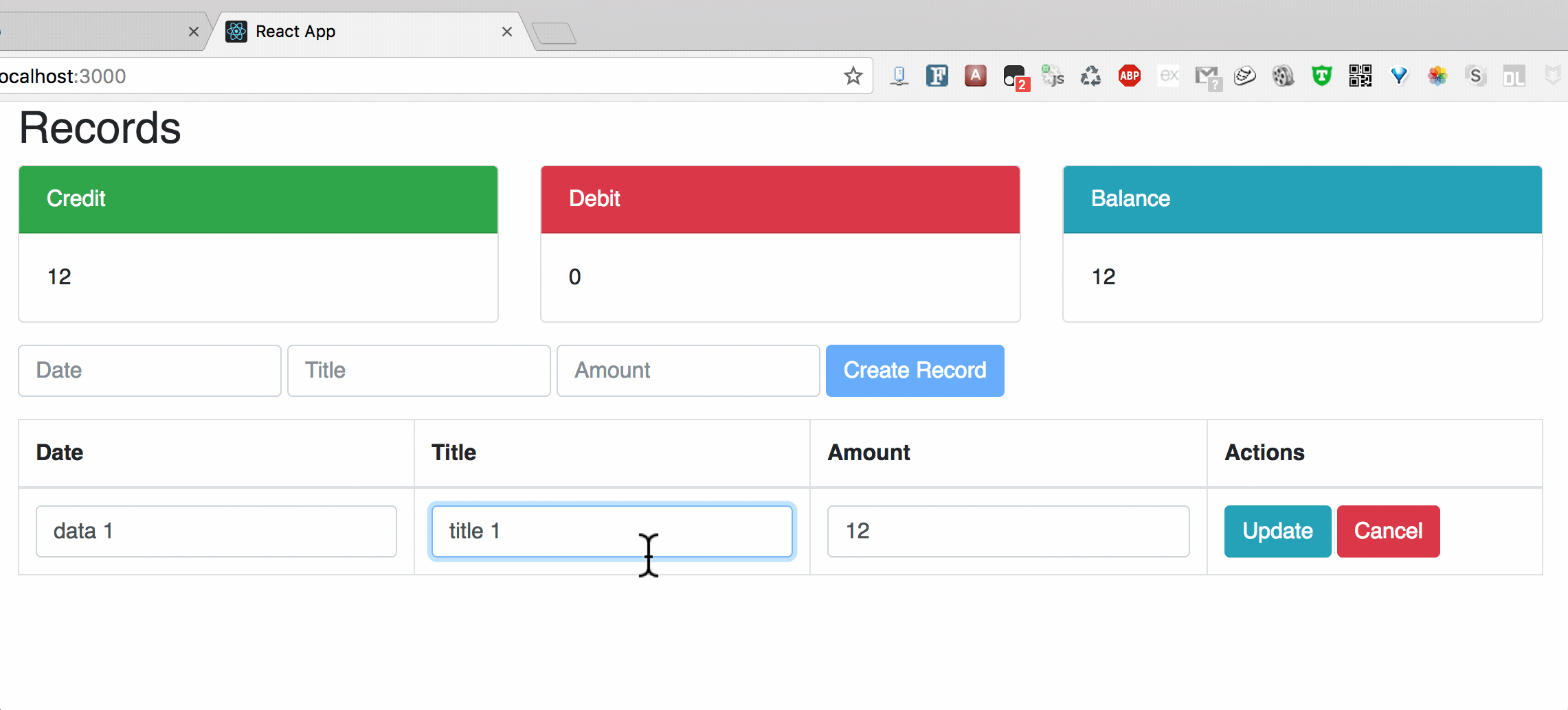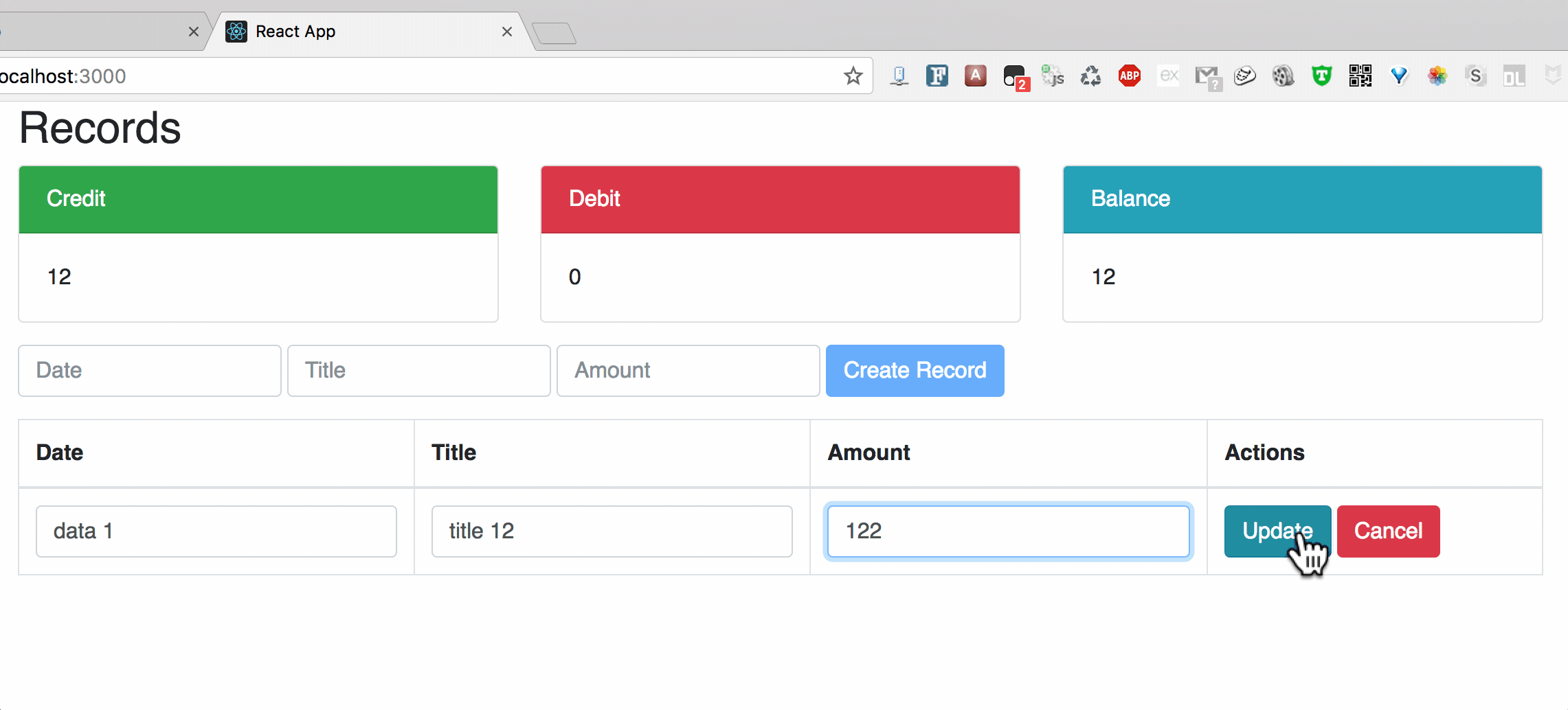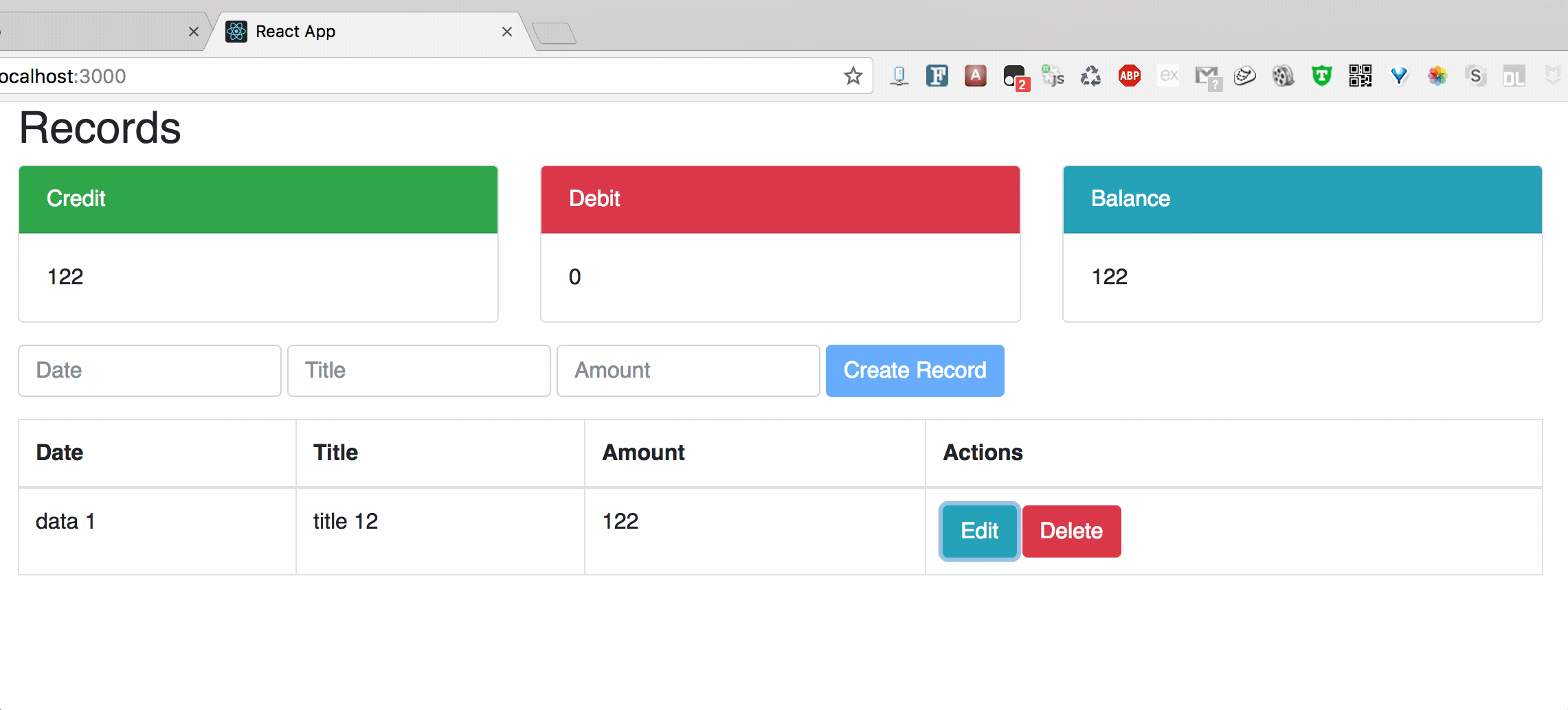
Chart3: Delete
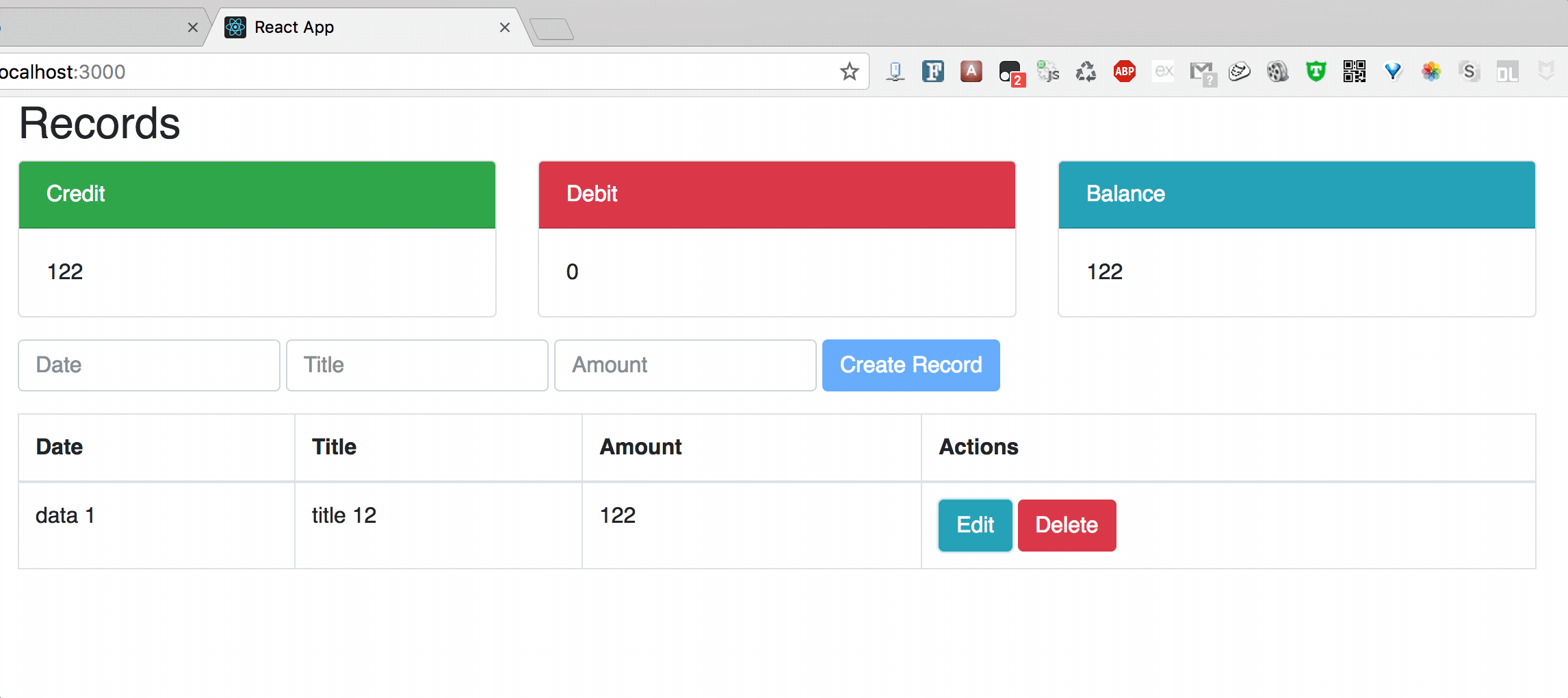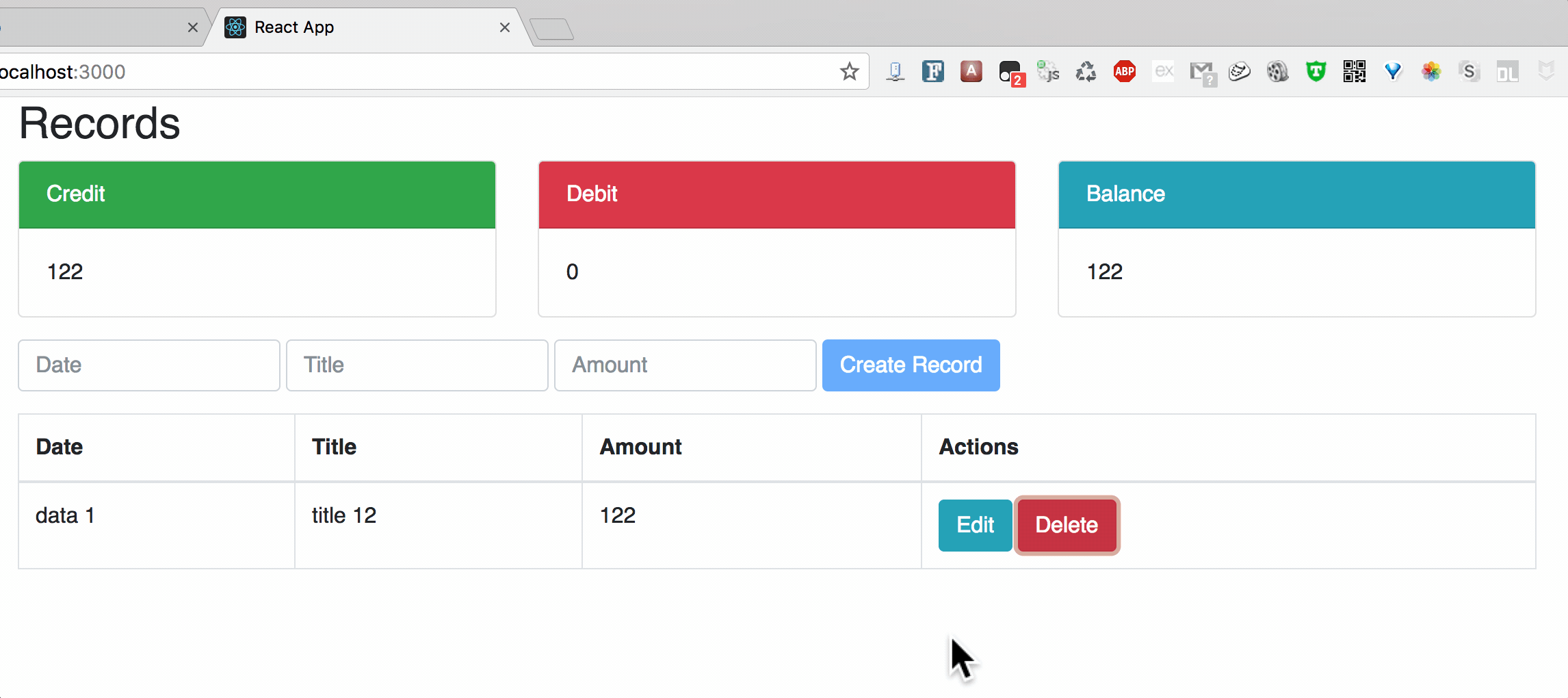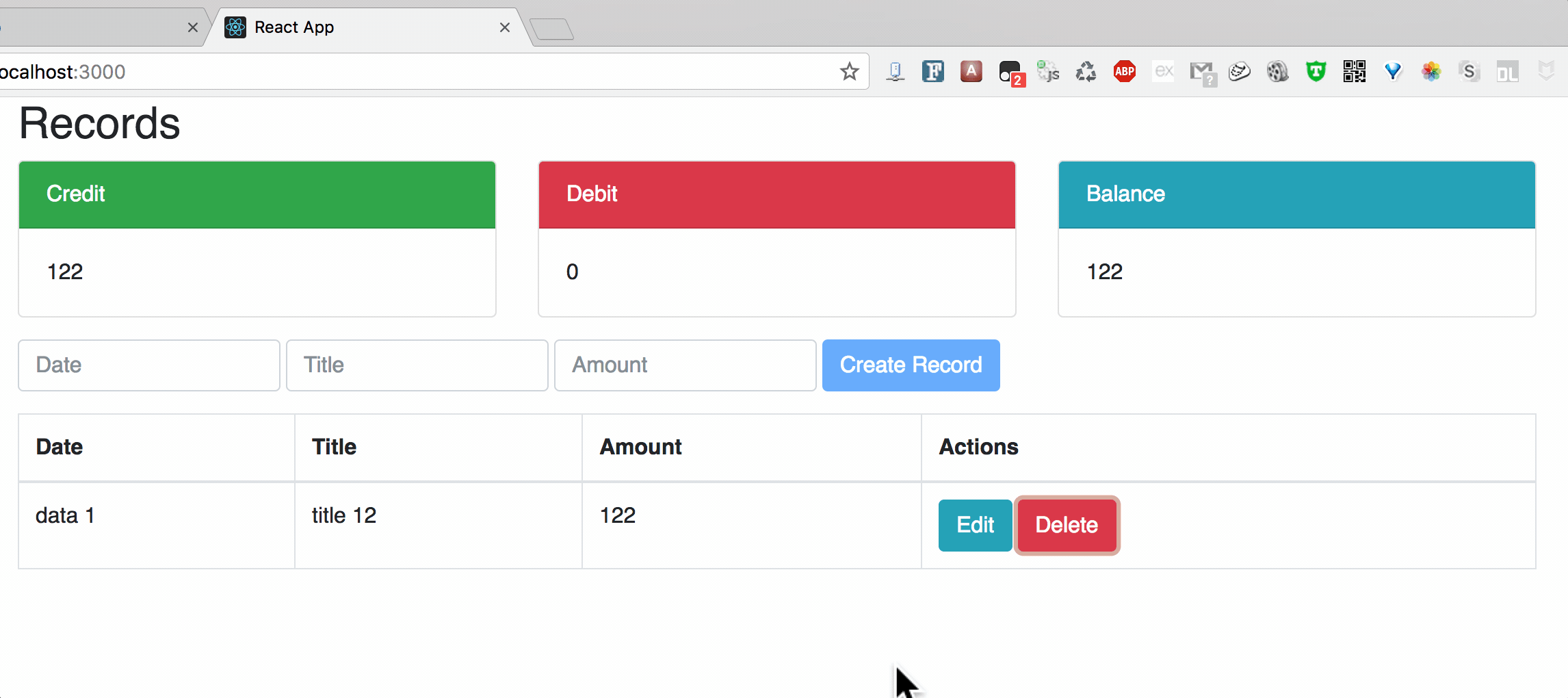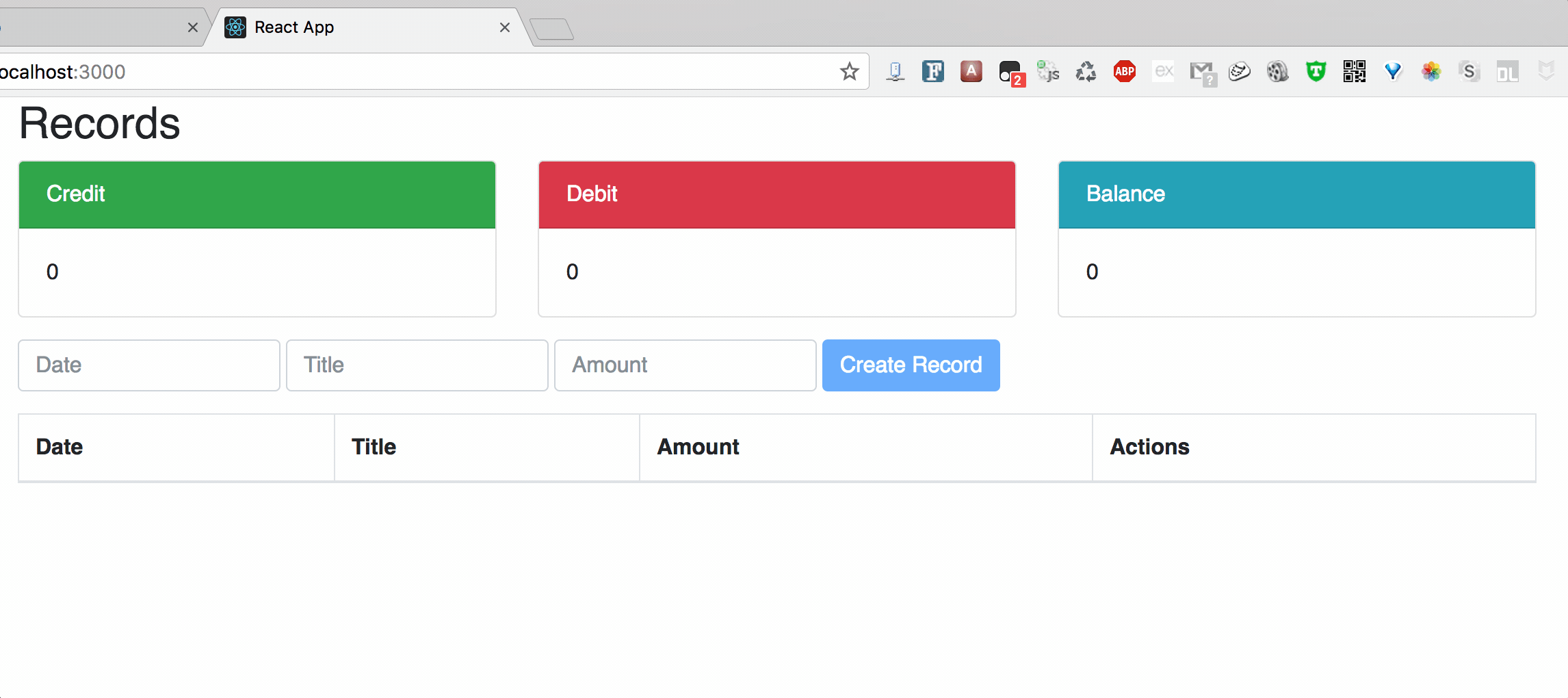
II. Structure
1. Components Structure
1 | App |
- App Component: is the data hub
- state:
recordsfor entries in Table component - state:
isLoadedshow loading info, before showing Table - state:
error - method:
componentDidMount()get data from database - method:
addRecord()passed to Form - method:
deleteRecord()passed to Table and TableRow - method:
updateRecord()passed to Table and TableRow - method:
credits()passed to Summary - method:
debits()passed to Summary - method:
balance()passed to Summary
- state:
- Summary Component: displays negative/ positive summation for the
records - Form Component: add
recordintorecords, updating Table - Table Component: just pass
recordsto TableRow - TableRow Component: display each
recordinrecords - RecordsAPI: utility providing interface to make RESTful API call
2. File Structure
1 | |__node_modules |
III. Ajax request
Several Ways:
- Ajax Libraries
- Axios
- axios.get(url[, config])
- axios.delete(url[, config])
- axios.head(url[, config])
- axios.options(url[, config])
- axios.post(url[, data[, config]])
- axios.put(url[, data[, config]])
- jQuery AJAX
- Axios
Browser built-in
window.fetchNo need to prepend “window” before
fetch(): default obj1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9## No need to prepend "window" before fetch, this is the default obj
fetch('http://example.com/movies.json')
.then(function(response) {
return response.json();
})
.then(function(myJson) {
console.log(myJson);
});
When and where to initiate Ajax call?
Do it in componentDidMount lifecycle method. So you can use setState to update your component when the data is retrieved.
1 | componentDidMount() { |
IV. Concept
1. 组件数据流: Model -> View
父组件M -> 子组件V
- 父组件prop 之间传给 子组件 prop
子组件M -> 父组件V
- 回调函数
- 父组件向子组件传递回调函数
- JS中,function是一等公民,因此传入的值会作为自身field保存起来;与C/Java不同。
- 回调函数
- sibling 组件间传值 M->V
- 必须依靠二者共同父组件来传递
- 但等组件之间的关系越来越复杂时候,这种依靠父组件作为中间人传值方式 would be a mess!
- Redux comes into picture
- 必须依靠二者共同父组件来传递
2. 双向绑定: Model <-> View
- 通过绑定
<input>的onChange()监视 View的变换 - 在 onChange Handler中更新组件的值,完成 View => Model 的数据流。
3. React 生命周期
- Mount
- constructor()
- componentWillMount()
- render()
- componentDidMount()
- Update
- componentWillReceiveProps(): 将接收新的props
- shouldComponentUpdate(): 是否应该被更新?
- componentWillUpdate(): 组件即将更新
- render(): 组件被渲染
- componentDidUpdate(): 组件完成更新
- Unmount
- componentWillUnmount(): 组件被卸载前做一些数据清除