I. Introduction
A MEAN stack Single Page Application, providing:
- URL shortening service
- Traffic statistics collecting service
Tech stacks: AngularJS, Node.js, Express, MongoDB, Redis, Nginx, Docker
Github: https://github.com/caomingkai/URL-shortening-service
II. Work flow
1. Users come to the app webpage
- Browser send GET request with original URL to server
- Server sends index.html to clients
- Browser get the index.html with script in the head tag.
<script src='angularJS library '> <script src='app.js'> <script src='/public/js/controllers/homeController.js'> - Browser again sends request for angularJS library/ js controller files to different servers
- when browser encounter ‘ng-view’, it automatically turn to ‘ng-router’, ask for its view and controller; Again, sends corresponding GET request to fetch sub-view files
- while browser parse the controller js file, it might do AJAX request to fetch information from server.
2. Users use the shortening service
- Input longURL in the input box, and click ‘submit’
- ‘submit’ fires the onclick funcion to do 2 things:
- send the longURL to specified URL, ie. POST to localhost/api/v1/urls
NOTICE: This url is specifically used for rendering short/long URL - send the longURL to specified URL, ie. POST to localhost/api/v1/urls
NOTICE: this step is executed after app server responds the POST request in the first step with the calculated shortURL
- send the longURL to specified URL, ie. POST to localhost/api/v1/urls
- App server first receive the POST request with longURL, do 2 things: call the urlService to calculate the shortURL, store long/short URL pair in MongoDB;send back the shortURL to the app webpage.
NOTICE: the shortURL should consist different prefix compared with the current app URL. Because it is create for outside users. So the shortURL should not prefix with /api/v1/.., but with just '/:shortUrl' - After the app webpage getting shortURL, it renders new subview using url.html; Meanwhile, it needs to know the its original longURL for display.
- Again, in the url.html subview, it sends GET request to the app server to get the longURL
Notice: This step could be simplified by just passing the longURL from the first subview to the second subview creating a service or using the $rootScop - Now, in the new subview, the longURL and shortURL pair can be displayed
3. Visitors browse the shortURL
- the shortURL is just clicked from various browsers/ machines/ from different IP/ countries, at different time
- when shortURL is clicked, it sends GET request ‘localhost/:shortUrl’ to the app server.
- the app sever call the urlService to get the longURL from the shortURL, and redirect users to the original long URL
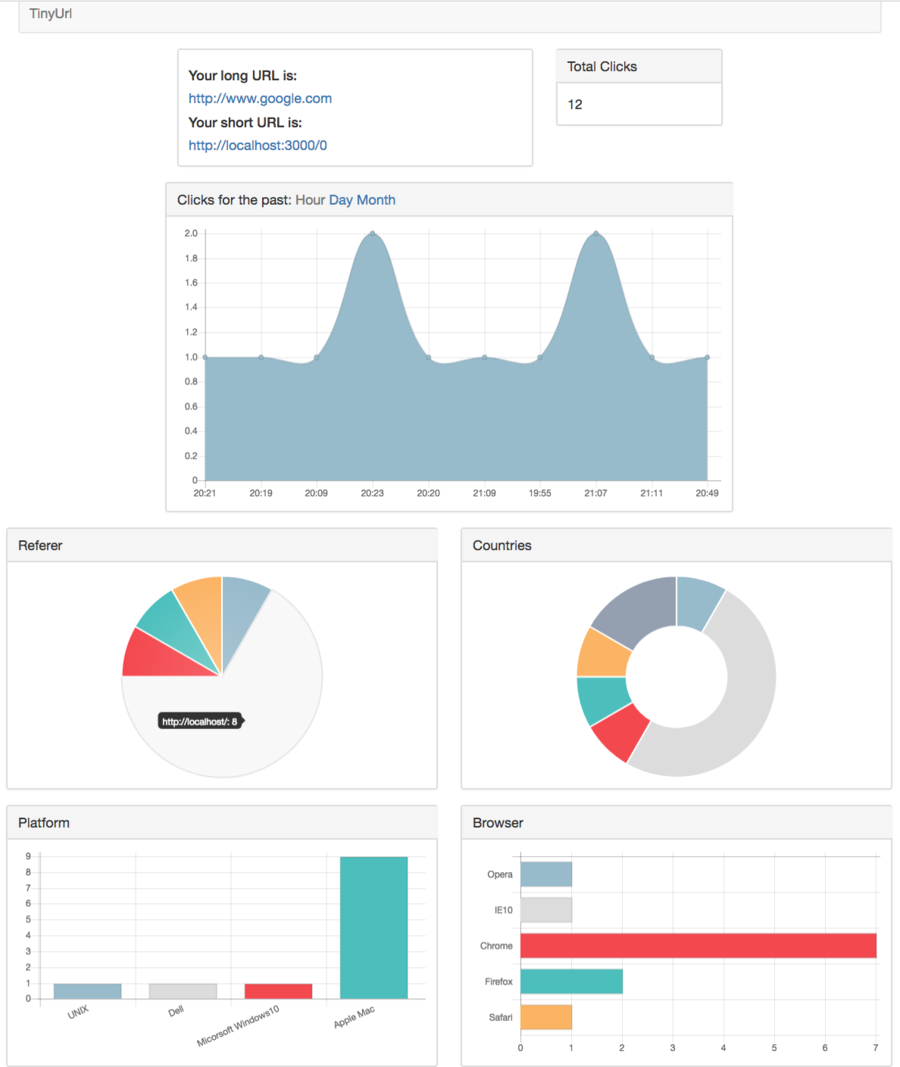
4. Traffic statistics Info
- We want to record the total number of clicks / their browsers/ machine brands/ their IP/ countries/ timestamp. And display them in the app webpage.
- So first we need add more elements in the url.html subview in the frontend; And update those information in the backend.
- updating the info each time the shortURL is clicked. And then store them in the MongoDB
- when app webpage is clicked, make AJAX call to the app server, let it get the info from MongoDB, and then send back to frontend
- Since all these clicks directly send GET request to ‘localhost/:shortURL’, which is handled by redirect.js. Thus, we here need a statistic service to update these info.
- Here we need the one of Express modules: Express-useragent to extract the information from the request
- In the statistic service, we use the express-useragent to get the info, and then store them in the MongoDB database with a new schema.
III. Nginx
Reverse Proxy
- (正向)代理forward proxy: 在client与internet之间,替client访问internet的计算机
- 路由器就是一个forward proxy,外网看不到路由器之后的计算机,但是计算机可以看到外边
- 翻墙服务器
- (反向)代理:在server与internet之间,替server接受internet访问的计算机
Features
- Hide Original server
“安全” - application firewall
- SSL termination: “加密不需要server进行,反向代理可以代为计算以减轻server压力”
- Load balance
- round robin
“optionally weighted” - least connected
“optionally weighted” - IP hash
“1~200: server a; 201~400: server b” - Generic Hash
“based on devices/ client locations” - Least time (nginx plux)
“optionally weighted”
- round robin
- Cache
- GET 都可以cache
- 即便是动态列表也进行cache,因为实际生活的改变不会比nginx的处理快 “1s <---> 100000 request/s”
- POST不能cache
- Compression(gzip)
“减小网络传输量: 用reverse proxy/ browser 的CPU为代价” - 不宕机进行配置改变/升级